Decentralised Finance (DeFi) is an umbrella term for a financial system built on blockchain technology. It aims to provide an open, permissionless, and decentralised alternative to traditional financial setups.
Compared to the conventional loan management process, DeFi lending does away with intermediaries, connecting the lender and the borrower directly.
The global decentralised finance market was valued at $13.61 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 46.0% from 2023 to 2030.
The growing acceptance of decentralised finance is revolutionising the financial sector. In this blog post, let us focus on its use in loan management.
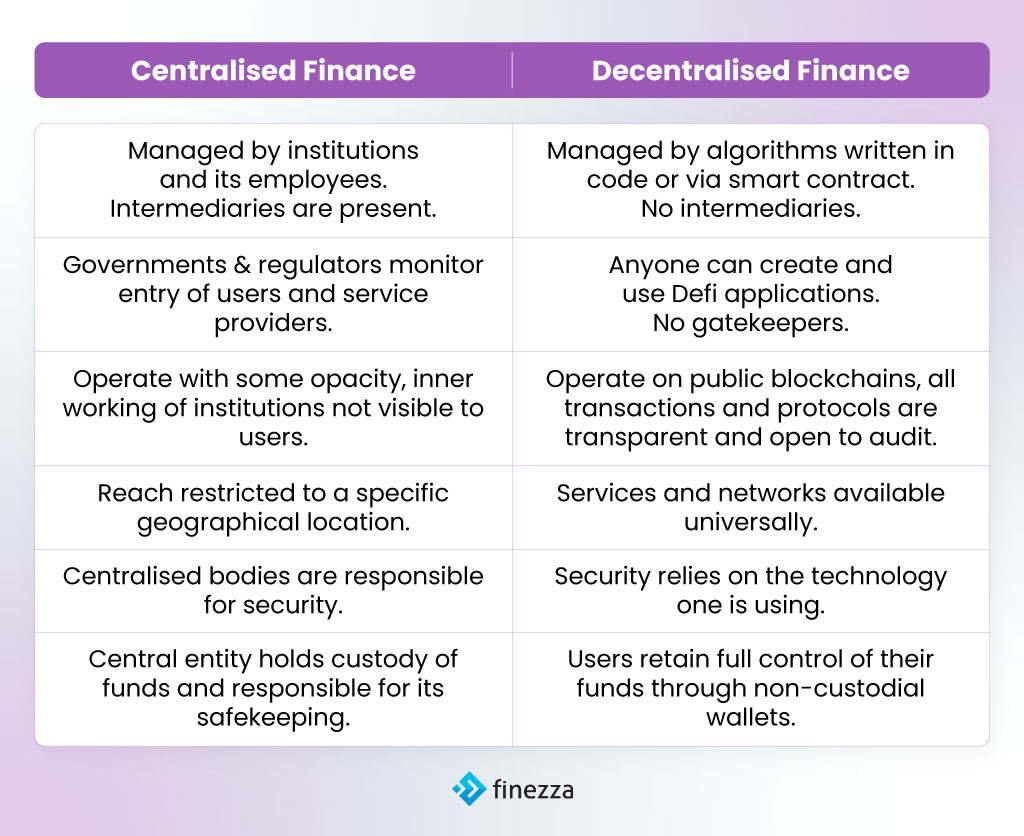
Decentralised Finance vs Centralised Finance: A Comparison
Under centralised finance (CeFi), governments control money flow, and banks control customers’ funds. In the context of loan management in India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governs which entities are authorised to provide loans to customers.
In contrast, decentralised finance operates without traditional intermediaries, such as banks or brokers, by using smart contracts on a blockchain.
Centralised Finance vs Decentralised Finance: A Table
An Overview of Decentralised Finance in Loan Management
DeFi is reshaping loan management, with lending protocols at its forefront. These open lending and borrowing platforms eliminate the need for traditional financial intermediaries like banks, allowing direct peer-to-peer transactions directly on open-source blockchain networks.
Borrowing in DeFi typically functions on a collateralisation model. Users deposit cryptocurrency as security for the loan they intend to borrow. The specific type and amount of collateral required depend on the loan terms and the platform’s policies.
This model enables transparent and efficient lending and borrowing processes within the DeFi ecosystem.
Features of DeFi loan management
- Smart Contracts: DeFi protocols utilise smart contracts to automate the lending process. These automated contracts manage essential functions such as determining interest rates, handling collateral, and enforcing repayment conditions, which enhances efficiency and reduces the potential for human error.
- No Intermediaries: Users can borrow and lend funds without the need for traditional banks or any other intermediaries. This permissionless access allows anyone with a crypto wallet to participate, irrespective of their geographical location or financial background.
- Collateral-Based Lending: The only requirement for accessing a loan is collateral, there are no additional requirements. Lending protocols do not require extensive identity checks like Know-Your-Customer (KYC) policies.
- Dynamic Interest Rates: These rates are an important feature of DeFi lending, they fluctuate in response to changing demand and supply and demand within the liquidity pool. Borrowers benefit from lower rates during periods of low demand but also face the risk of rates increasing when demand spikes.
Loan Management: The Potential of Decentralised Finance
DeFi has the potential to benefit individual users and the entire economy. Here are some ways it brings about a positive impact:
1. Promotes Inclusivity and Accessibility
DeFi loans have low entry barriers; there is no requirement for traditional credit scores or extensive documentation, which frequently restricts access for many. The underserved often cannot access credit due to a lack of documentation, credit history or absence of banking channels in the vicinity. DeFi remedies this challenge, as only an internet connection and a digital wallet are required to access a loan.
DeFi platforms connect borrowers directly with lenders, doing away with traditional credit check processes, thereby, promoting financial inclusion. They operate 24/7, offering continuous and uninterrupted access to users, who can avail of the services anywhere, anytime. Loan management through DeFi platforms helps empower the underbanked and unbanked individuals.
2. More Efficiency and Reduced Cost
DeFi eliminates manual processes and paperwork in loan management. Smart contracts automate loan processing, repayment and collateral management leading to faster transactions and lower costs. This reduces errors and streamlines loan approvals, asset transfers, and trade settlements.
On the other hand, global accessibility eliminates geographic barriers and reduces the need for multiple intermediaries involved in cross-border transactions.
3. Improves Transparency and Security
Defi platforms operate on public blockchains; they are publicly observable and the smart contract codes can be analysed on the blockchain. Anyone can audit the transactions and contracts, helping reduce the chances of fraud and risk.
Self-executing smart contracts, which have the terms of the agreement directly written into code reduce the need for trust between parties. The contracts are enforced automatically, leaving no scope for manipulation and breach.
4. Interoperability
Many DeFi protocols are designed to be interoperable, enabling users to move assets seamlessly across different platforms.
5. Community Governance
DeFi platforms often allow token holders to vote on important decisions, such as protocol upgrades and lending policies. This participatory approach empowers the community and aligns the platform’s operations with user interests.
6. Risk Management and Analytics
By analysing loan performance data, DeFi platforms can refine their lending criteria and enhance service quality, ultimately leading to better outcomes for both borrowers and lenders.
Loan Management via Decentralised Finance: Challenges and Risks
DeFi offers numerous benefits and holds tremendous potential for the future. However, certain inherent risks cannot be ignored:
1. Vulnerable Consumers
The absence of a regulatory authority or clear guidelines within the DeFi space leaves users with limited options in case of a dispute or a transaction gone wrong.
2. Cyber risks
DeFi’s reliance on software and smart contracts makes it vulnerable to hacking and exploits, potentially leading to significant financial losses. Users must be aware of these emerging risks and take precautions when interacting with DeFi protocols.
3. Collateralisation
While DeFi loans have no entry barriers, the collateral makes them out of reach for some. Collateral is required to secure a loan and almost all DeFi lending transactions require collateral equal to at least 100% of the loan value. This vastly restricts who can avail of these loans.
Final Note
While DeFi is still in its early stages, both centralised finance and DeFi bring unique qualities and applications to the table. They share a common goal: to provide valuable financial services and products, ultimately contributing to economic growth.
Technological breakthroughs and innovative tools will likely continue to fuel growth and evolution in both the CeFi and DeFi ecosystems, offering exciting possibilities for the future of finance.
As a Lending Lifecycle Management Platform, Finezza offers a suite of products for loan management that leverage emerging technology like artificial intelligence, data analytics, machine learning and more for lenders.Contact us to know more.



Leave a Reply